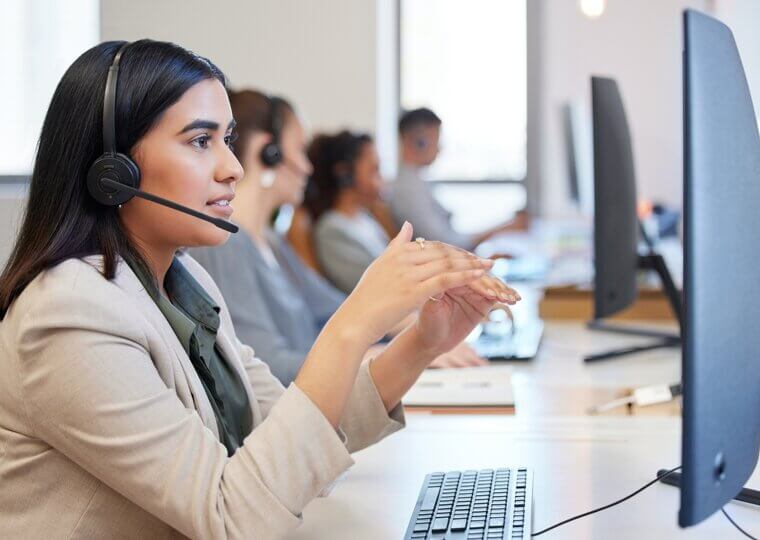
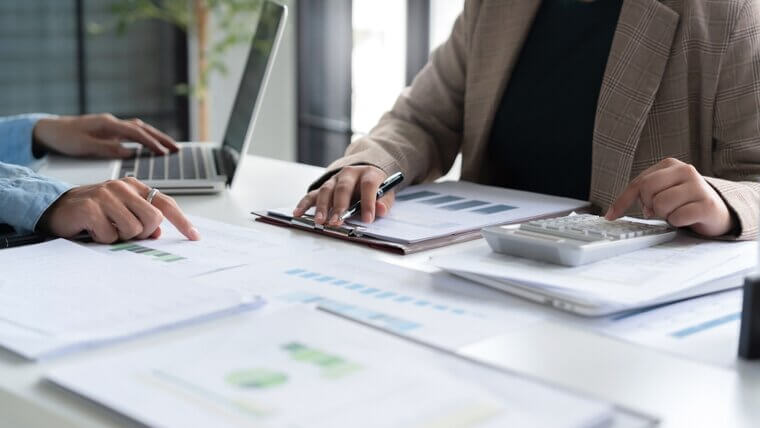
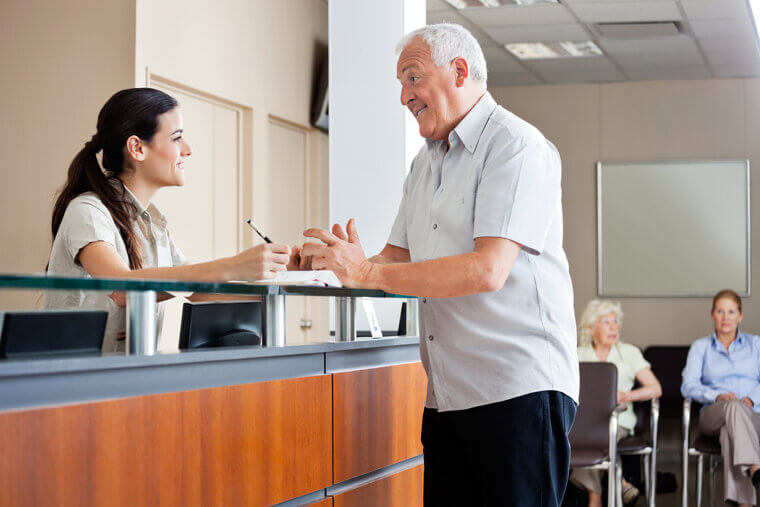
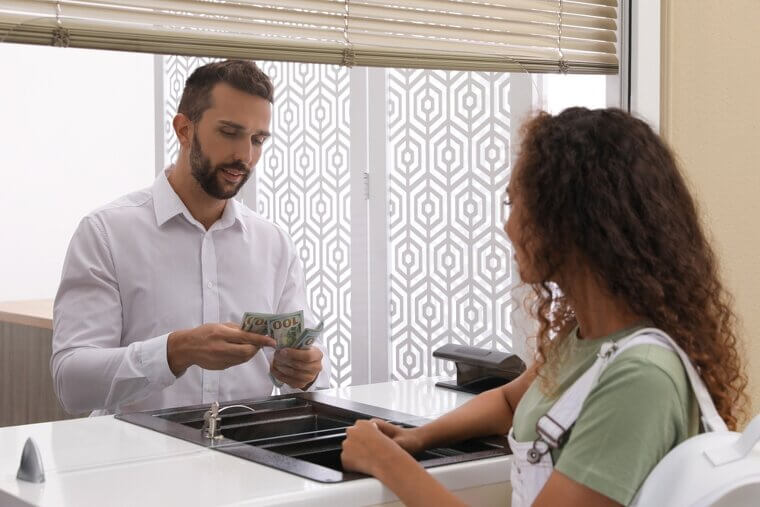
Telemarketers
With AI’s rapid advancements in customer interaction software, telemarketing roles face high automation potential. AI-powered systems can now efficiently conduct outbound calls, answer questions, and make sales suggestions. These platforms operate 24/7 and are programmed to improve over time by learning from each interaction, delivering consistent messaging without fatigue or errors. For businesses, using AI over human telemarketers reduces overhead costs while maintaining a steady volume of outreach.
Although some consumers still prefer speaking with a person, as AI becomes more sophisticated in mimicking human conversation, telemarketers are likely to find fewer opportunities in an AI-dominated field.
Bookkeeping Clerks
AI’s capacity to process financial transactions and maintain digital records has made bookkeeping one of the most automatable jobs. Systems like QuickBooks and Xero use machine learning to classify expenses, handle invoicing, and reconcile accounts with minimal human intervention. By automating these repetitive and error-prone tasks, AI increases accuracy and saves companies significant time and costs. While specialized accountants still hold value, bookkeeping clerks are increasingly redundant in modern workplaces.
As companies continue to adopt AI for real-time financial tracking and reporting, bookkeeping roles may shrink, with AI gradually taking on a larger role in day-to-day finance management.
Receptionists
AI-driven virtual receptionists, automated scheduling systems, and chatbots are transforming front-desk management, gradually replacing traditional receptionist roles. These systems efficiently manage calls, book appointments, and answer common inquiries, handling tasks that once required human interaction. Virtual assistants like Google Assistant and Alexa further streamline customer service, managing both internal and external queries with ease. For many companies, AI receptionists reduce costs, operate 24/7, and minimize the risk of human error.
While clients might prefer a human touch, AI’s adaptability and round-the-clock availability make it a competitive option, especially in industries focused on optimizing efficiency and customer experience.
Bank Tellers
Traditional bank teller roles are increasingly automated with AI technologies such as digital banking and smart ATMs, which can handle deposits, withdrawals, and even complex transactions without human help. Many banks now offer mobile apps and web-based platforms that perform routine transactions once handled by tellers. This shift not only reduces wait times but also provides customers with flexibility in managing finances, a win-win for everyone involved.
While there will always be a need for personalized services in banking, AI-driven digital solutions are poised to dominate most standard banking interactions, making human tellers less essential, especially as younger generations prefer online banking.
Customer Service Representatives
AI chatbots and virtual assistants are reshaping customer service, handling routine inquiries, troubleshooting, and even sales. With advancements in natural language processing, AI can understand and respond to customer queries effectively, improving response times and consistency. These systems provide 24/7 support, which is increasingly favored by businesses for cost-efficiency and accessibility. Although human representatives are still needed for complex or sensitive issues, AI’s role in customer service continues to expand.
As more companies integrate AI-driven customer support, the demand for human customer service roles is anticipated to decline, especially for repetitive tasks like order inquiries and account management.
Cashiers
Self-checkout kiosks, mobile payment solutions, and AI-driven point-of-sale systems are transforming retail environments, reducing the need for human cashiers. Customers can scan, bag, and pay for their items independently, with AI providing real-time assistance if needed. In addition to enhancing the customer experience, this technology lowers labor costs for businesses and speeds up transactions. As more retailers adopt AI and automation in payment processes, cashiers are becoming less essential.
Although some stores still rely on human staff for a personal touch, the push toward automation is unmistakable, particularly in large retail chains where efficiency and speed are prioritized.
Data Entry Clerks
AI’s ability to accurately process and organize data has made data entry one of the most automatable functions. Automated data capture systems now extract information from documents, forms, and emails, reducing human errors and speeding up entry processes. Many companies are transitioning to AI-powered platforms for data processing, reducing the need for manual data entry and enabling faster decision-making. This shift to automation in data management not only cuts operational costs but also allows businesses to handle larger volumes of data.
As AI improves, the need for data entry clerks is expected to continue its decline across industries. It might be a good time to start looking for other skills and experiences for those in this position.
Market Research Analysts
AI-driven analytics tools can quickly process market data, identify trends, and even predict future consumer behaviors, tasks traditionally done by market research analysts. By analyzing vast datasets in real-time, AI can provide insights into customer preferences and forecast market shifts. These capabilities streamline decision-making processes for businesses, which might previously have taken days or weeks of manual analysis. Although human oversight remains necessary to interpret findings and apply insights contextually, the need for extensive manual research is reduced.
This shift enables businesses to make data-informed decisions faster, potentially minimizing demand for human analysts in favor of AI solutions.
Computer Support Specialists
AI in IT support now handles routine troubleshooting and technical support tasks. Automated chatbots diagnose issues like connectivity problems, password resets, and software malfunctions. These AI systems operate around the clock, minimizing downtime for businesses and reducing reliance on entry-level IT support roles. By analyzing past issues and solutions, AI can continually improve, offering more precise assistance over time. Although complex issues still require human expertise, the need for this will decrease.
The reliance on human computer support specialists is decreasing as companies invest in AI-driven IT support to handle basic tech support needs more efficiently.
Advertising Salespeople
AI algorithms excel in analyzing audience data and optimizing ad placements, reducing the need for traditional ad sales roles. These tools can manage ad budgets, target specific demographics, and monitor campaign performance in real-time, allowing for more effective and data-driven advertising. With AI’s growing ability to personalize ad content and distribution strategies, companies can achieve greater reach and engagement with minimal human intervention. Although creative strategy roles remain essential, the operational side of ad sales is increasingly dominated by AI.
This increase in AI systems will shift the landscape of digital advertising and potentially decrease opportunities for human sales agents.
Retail Salespeople
As online shopping platforms increasingly dominate retail, traditional in-store retail sales roles are being impacted. AI tools personalize customer recommendations, track inventory, and even handle payment processing, allowing customers to shop without assistance. Online AI chatbots now help customers find products, answer questions, and even cross-sell items based on browsing history. With large retail chains introducing cashier-less stores, the role of in-store retail salespeople is evolving.
While human interaction remains important for specialized products and customer loyalty, AI-driven e-commerce and in-store automation are gradually reducing the demand for retail staff in favor of digital customer engagement solutions.
Drivers (Truck and Delivery)
AI and autonomous vehicle technology are advancing rapidly in logistics, especially with driverless trucks and delivery drones. Companies are testing self-driving trucks that can handle long-haul transportation, reducing the need for human drivers. Autonomous delivery drones and robots have also emerged, transforming last-mile delivery in urban areas. AI systems analyze traffic patterns, optimize routes, and improve fuel efficiency, making logistics more cost-effective and reliable - not to mention quicker.
While safety and regulatory challenges still limit full implementation, the transportation industry is shifting toward automation. These advancements indicate that many routine driving and delivery jobs could be significantly affected by AI in the coming years.
Couriers
The demand for human couriers is decreasing with the rise of AI-powered drones and autonomous robots. Companies are increasingly adopting drones to handle local deliveries, especially for small, time-sensitive packages. Automated delivery systems operate faster and around the clock, improving efficiency and reducing costs for companies. AI-based logistics platforms also help optimize delivery schedules and routes, minimizing human input in the decision-making process. While this might result in less jobs in the field, it will also make the entire system faster.
While human couriers are still needed in rural or complex urban settings, automated systems are expected to take over routine delivery routes in cities, gradually replacing a significant portion of traditional courier roles.
Proofreaders
AI-driven grammar and style-checking tools, such as Grammarly and ChatGPT, are transforming the proofreading landscape by automating the review of grammar, syntax, and even tone. These tools can scan and correct documents more quickly and accurately than many human proofreaders, making them invaluable for high-volume editing tasks. Additionally, AI can learn from user preferences, allowing it to tailor corrections for consistency. While experienced editors may still be required for nuanced and context-sensitive editing, especially in creative fields, the routine work of proofreaders is becoming increasingly automated.
This rise in automations, thanks to AI, will reduce the need for human input on basic proofreading tasks, potentially completely replacing this role eventually.
Legal Researchers
AI tools for legal research are advancing, automating the time-intensive task of searching through case law, statutes, and legal precedents. Platforms like LexisNexis and Westlaw Edge use AI to sift through vast legal databases, identifying relevant information and even suggesting legal arguments. This capability dramatically reduces the time needed for traditional research tasks and decreases the reliance on entry-level legal researchers. Although experienced legal professionals still oversee and interpret findings, much of the manual work is now handled by AI.
This helps reduce labor costs in law firms. This shift is redefining roles in legal research and diminishing demand for junior researchers.
Financial Analysts
AI-driven platforms can analyze stock patterns, economic data, and financial metrics at a speed and accuracy level unmatched by human analysts. These tools, using machine learning, predict market trends and assist in investment decision-making by quickly processing large volumes of historical and real-time data. AI reduces the need for routine financial analysis by providing data-backed insights, which were once the primary role of financial analysts. While human oversight remains necessary for complex interpretation, risk assessment, and client communication, AI’s role in financial analysis is rapidly expanding.
This leaves fewer traditional roles for financial analysts, especially in high-volume trading environments, meaning it's a role at risk of being replaced by AI.
Claims Adjusters
AI technology is transforming insurance claims by automating the evaluation process. AI algorithms can quickly review and process data related to claims, assessing damage and identifying potential fraud. Insurance companies benefit from AI’s ability to streamline claims processing, resulting in faster resolutions and fewer manual tasks. For simpler cases, AI can fully automate claim decisions, reducing the need for human adjusters. Luckily, more complicated cases will still require human touch - at least in the near future.
Although complex cases and client interactions still require human judgment, the demand for claims adjusters is decreasing as AI enhances efficiency and accuracy in the insurance industry.
Insurance Underwriters
AI tools are increasingly employed in insurance underwriting to assess risk profiles based on historical data and statistical models. AI can analyze large datasets more accurately and consistently than human underwriters, streamlining risk assessment and policy pricing. Automated underwriting systems are especially effective in areas such as life, health, and auto insurance, where data patterns are critical in determining risk. While complex underwriting may still require human judgment, much of the preliminary assessment work can be automated.
Automating so much of the workload will reduce the need for traditional underwriters and speed up the policy approval process.
Loan Officers
Automated loan assessment platforms are increasingly replacing traditional loan officers for basic loan processing tasks. AI evaluates applicants’ credit scores, employment history, and financial background to determine loan eligibility within seconds, reducing wait times for clients and processing costs for banks. Although high-value loans and complex cases may still involve human oversight, AI systems handle routine loan applications with efficiency and accuracy, often minimizing the need for traditional loan officers in personal and small business banking.
As these systems become more reliable, the role of loan officers is expected to continue shrinking as companies implement more and more AI.
Accountants
AI-driven accounting platforms now automate many routine tasks, such as expense tracking, tax preparation, and financial reporting, reducing the need for human accountants in basic roles. These tools can categorize expenses, calculate taxes, and generate reports, making daily accounting processes more efficient and accurate. While complex financial analysis and strategic advising still require human input, small businesses and individuals increasingly rely on AI to handle day-to-day accounting.
This shift in demand, combined with ongoing advancements in AI-driven financial tools, is expected to reduce the number of traditional accounting roles over time.
Paralegals
Paralegals handle a large volume of documentation, research, and routine tasks that AI can streamline. AI-powered tools are adept at searching legal databases, identifying relevant case laws, and preparing initial drafts, all of which were once manual tasks managed by paralegals. Software like e-discovery tools now perform much of the research and documentation preparation work, making complex legal case data manageable and accessible in minutes. This technology reduces time and costs for law firms, meaning that fewer entry-level paralegals are required.
However, complex interpretation, client interaction, and high-level case strategy still rely on human oversight. The trend toward automating repetitive paralegal tasks points toward an evolving but reduced role for human paralegals.
Medical Transcriptionists
With advancements in voice recognition software, medical transcription has become one of the most affected professions by AI. Speech-to-text programs, such as Dragon Medical One, can transcribe doctors' notes, patient interactions, and diagnoses with remarkable accuracy, reducing the need for human transcriptionists. These tools allow healthcare providers to input information directly into electronic health records, streamlining documentation and improving workflow efficiency. AI systems not only save time but also minimize errors in transcription by applying medical terminology databases, allowing for instant verification of terms.
As speech recognition technology continues to improve, it is likely that demand for traditional medical transcriptionists will decline significantly in healthcare.
Inventory Managers
AI and automation are transforming inventory management, traditionally a role dependent on human oversight. AI-powered inventory systems track stock levels, forecast demand, and even reorder supplies as needed without human intervention. Machine learning algorithms analyze past sales data to predict which products will be in demand, enabling businesses to optimize their stock levels and reduce waste. Automated tracking tools provide real-time visibility into inventory across multiple locations, eliminating manual checks and reducing the margin for error.
This technology enhances supply chain efficiency, minimizing the need for traditional inventory managers, particularly in large retail and distribution networks where high volumes require precise control.
Library Technicians
Library technicians, who handle cataloging, record management, and other administrative tasks, are seeing parts of their roles automated by AI. Automated cataloging systems and digital management tools can now sort, categorize, and tag library resources efficiently, making it easier for patrons to access materials online. Additionally, AI chatbots are being introduced in libraries to answer user questions, recommend resources, and assist with digital book lending.
While librarians who offer community services and educational programs are still essential, the core duties of library technicians, such as managing inventory and catalog records, are increasingly taken over by AI and digital tools, reducing the need for traditional roles in large library systems.
Quality Control Inspectors
AI’s visual recognition capabilities have transformed quality control, especially in manufacturing where tasks such as defect detection are critical. Automated visual inspection tools and AI-driven sensors can detect inconsistencies or defects in products with high precision, reducing the need for human inspectors. These systems continuously monitor production lines, identifying issues in real-time and ensuring quality standards without fatigue. AI can also analyze trends and predict failures before they occur, allowing manufacturers to make proactive adjustments.
Although complex evaluations may still require human judgment, AI has taken over much of the routine inspection work, particularly in industries like automotive and electronics, where quality control is essential.
Assembly Line Workers
Automation has long been a feature in manufacturing, but AI takes it further by optimizing assembly line tasks that require repetitive actions. Robotics equipped with AI can perform assembly tasks with precision and consistency, from welding parts to packaging products. AI algorithms monitor the workflow and make adjustments to maximize efficiency, handling a higher output than human workers with minimal error rates. This trend is particularly evident in sectors such as automotive and electronics manufacturing, where accuracy and speed are crucial.
Human oversight is still needed for troubleshooting and oversight, but AI is quickly replacing many manual assembly roles.
Loan Interviewers
Loan interviewers handle initial applicant screening, a task increasingly automated by AI-based loan processing systems. These platforms assess applicant eligibility using credit scores, employment history, and financial background in real time, enabling faster and more consistent loan approval decisions. This level of automation not only shortens wait times for applicants but also reduces the need for human interviewers. Advanced AI systems can also detect fraud and ensure compliance, allowing banks and financial institutions to streamline operations.
Human loan interviewers may still handle complex cases or high-value loans, but the demand for entry-level roles is declining as banks turn to automated solutions.
Tax Preparers
AI tax software, such as TurboTax and H&R Block, allows individuals and businesses to file taxes without needing a tax preparer. These platforms analyze tax codes, calculate deductions, and fill out forms automatically, reducing the time and errors associated with manual tax preparation. Advanced AI programs can even flag potential deductions or errors, streamlining tax filing for users. For most standard filings, AI handles everything, making tax preparation services less essential.
While complex tax cases and high-income individuals may still require human expertise, AI is reducing the demand for traditional tax preparers, particularly among small businesses and individual filers.
Social Media Managers
AI-driven tools are revolutionizing social media management by automating content scheduling, analytics, and audience engagement. Platforms like Hootsuite and Buffer use AI to recommend optimal posting times, analyze engagement metrics, and even generate content ideas. Additionally, chatbots are being used to handle customer inquiries and comments on social media, allowing companies to maintain an active online presence without a human manager. While strategic planning and brand voice management still benefit from human oversight, AI systems handle much of the operational work in social media.
AI systems are then reducing the need for entry-level social media managers and enabling more efficient content management.
Travel Agents
Online booking platforms and AI-powered trip planners are reducing the demand for traditional travel agents. Platforms like Expedia and Google Flights use predictive algorithms to suggest optimal booking times and recommend accommodations based on customer preferences. AI chatbots assist travelers in planning trips, comparing prices, and making reservations without requiring human help. Additionally, virtual assistants can provide destination information, manage bookings, and even offer travel tips, making trip planning more accessible and convenient.
While luxury travel planning and customized itineraries may still require human expertise, routine travel arrangements are increasingly handled by AI, diminishing the need for traditional travel agents.
Real Estate Brokers
AI is transforming real estate with data-driven insights and automated customer service tools that assist buyers in their search. Real estate platforms like Zillow and Redfin use AI to analyze market trends, property values, and client preferences, helping buyers find relevant listings without a broker. AI chatbots guide customers through property searches, answer questions, and even schedule viewings. While negotiations and high-value sales may still require human agents, AI tools are taking over routine tasks and more.
AI systems are providing clients with real-time insights and reducing the need for traditional brokers, especially for entry-level roles in high-volume property listings.
Advertising Copywriters
AI-powered content generators, such as ChatGPT, are capable of creating marketing copy for various platforms, reducing the need for human copywriters. These tools can generate product descriptions, social media captions, and even ad slogans, allowing brands to maintain a consistent online presence without hiring full-time writers. With machine learning, AI tools adapt to brand guidelines and target audience preferences, producing copy that meets specific marketing goals.
While creative strategy and nuanced storytelling still require human input, many operational writing tasks are now managed by AI, reducing demand for entry-level advertising copywriters, particularly for basic ad content.
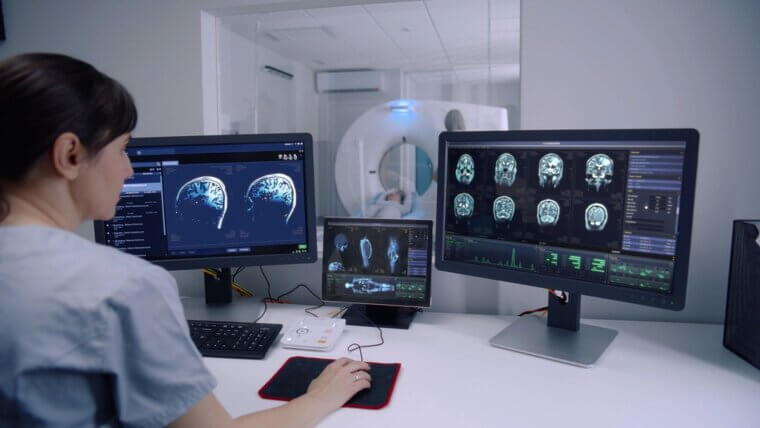
Radiologists
AI’s role in medical imaging is growing, with advanced algorithms capable of detecting abnormalities in X-rays, CT scans, and MRIs. These tools assist radiologists by flagging potential issues, allowing for faster and more accurate diagnoses. AI systems learn from vast datasets, which enables them to identify even subtle signs of disease. While AI is not yet capable of fully replacing human radiologists, it significantly reduces the time needed to review scans.
In routine cases, AI may eventually handle most initial diagnostics, leaving radiologists to focus on complex or ambiguous cases, thus reshaping the role rather than entirely replacing it.
Credit Analysts
AI platforms are increasingly used in finance to assess credit risk, analyzing factors like credit history, income, and spending behavior. These platforms allow financial institutions to make faster and more consistent lending decisions by eliminating human biases and using real-time data. AI systems can flag high-risk applicants and predict future creditworthiness with greater precision than traditional methods. While complex cases may still require human insight, AI’s ability to manage high volumes of credit applications reduces the need for human credit analysts.
This is particularly true in large banks and lending institutions where efficiency and speed are prioritized and AI systems are more likely to be implemented widely.
Security Guards
Automated security systems, such as surveillance drones and AI-powered cameras, are increasingly used for monitoring premises without the need for human guards. These systems use motion detection, facial recognition, and real-time alerts to identify potential security threats. Drones can patrol, monitor extensive areas, and respond to incidents. AI cameras analyze footage continuously, alerting human supervisors only when anomalies are detected. While human guards are still essential in high-security environments, many roles are now focused on managing and overseeing AI systems rather than patrolling premises.
These automated systems reduce the need for large security teams, with AI playing a significant role in minimizing human errors and enhancing response time. As companies prioritize cost efficiency and comprehensive surveillance, AI-driven security solutions are expected to replace many traditional guard duties, particularly in corporate and large public settings.